Abstract
Introduction
Treatment of CLL is rapidly evolving, now including oral targeted agents and novel combinations. However, complete response (CR) rates remain low and continuous therapy is required. Eradication of minimal residual disease (MRD) is an increasingly important endpoint and an independent predictor of improved survival.
Lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel; JCAR017) is an investigational CD19-directed 4-1BB CAR T cell product administered in a defined composition of CD8:CD4 CAR T cells. TRANSCEND CLL 004 is an open-label Phase 1/2 trial of liso-cel in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL (NCT03331198). Preliminary safety, pharmacokinetic (PK), and efficacy results from the Phase 1 monotherapy dose-finding portion of this study are reported.
Methods
Pts with CLL/SLL were eligible if they had received 3 (standard risk) or 2 [high risk: del(17p), TP53 mutation, unmutated IGVH, or complex karyotype] prior lines of therapy, including a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) unless medically contraindicated. Pts with active untreated CNS disease, ECOG >1, or Richter's transformation were excluded.
After 3 days of lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, pts received liso-cel infusion. Two dose levels (DL) have been tested (DL1=5 × 107 CAR T cells; DL2=1 × 108 CAR T cells). Dose escalation followed a modified toxicity probability-interval-2 (mTIPI-2) algorithm. Dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) were evaluated for 28 days post liso-cel infusion.
Responses were assessed by iwCLL 2008 criteria. MRD was assessed at 10-4 sensitivity by 6-color flow cytometry using peripheral blood and at 10-6 sensitivity by clonoSEQâ (Adaptive) deep sequencing of bone marrow (BM) aspirates. Blood PK of liso-cel was determined using flow cytometry. Serum soluble chemokine and cytokine profiles for 39 analytes were assessed using V-PLEX immunoassays (MSD).
Results
At the time of data cut, 10 pts received liso-cel: 6 pts treated with DL1 and 4 pts with DL2. The median age was 64.5 years (range 51-76); 7/10 pts had high-risk disease. Pts had received a median of 4 prior therapies (range 3-8), including 9/10 pts who had received prior ibrutinib and 6/10 who previously received venetoclax and ibrutinib.
No DLTs were identified. The most common adverse events (AEs) were cytokine release syndrome (CRS) (8/10 pts; all grade [G] 1/2), anemia (7/10 pts), thrombocytopenia (6/10 pts), and leukopenia (5/10 pts). Neurologic events (NE) were reported in 3/10 pts: G1 impaired concentration and aphasia, G3 encephalopathy, and G3 aphasia. The median time to onset of CRS and NE was 4.5 (range 1-9) and 11 (range 11-21) days respectively, and the median duration of CRS and NE was 5.5 (range 3-30) and 6 (range 2-20) days respectively. Six pts received tocilizumab and/or steroids for the management of CRS and/or NE. Serious AEs, all of which were G3/4, were reported in 5/10 pts.
At 30 days post-dose, 6 of 8 pts who were evaluable for response had an objective response (75%), including 4 CRs (50%). Six of 7 pts (85.7 %) evaluable for MRD had undetectable disease by flow at the day 30 assessment. Of the 5 pts evaluable for response at 3 months post-dose, 4 had ongoing response and 1 progressed with Richter's transformation. All 4 pts with ongoing response continued to have undetectable MRD by flow at 3 months post-dose. Responses, including CRs and undetectable MRD responses, occurred in pts with high-risk and with standard-risk disease. Available BM analyses from clonoSEQâ data corroborate these findings and will be reported.
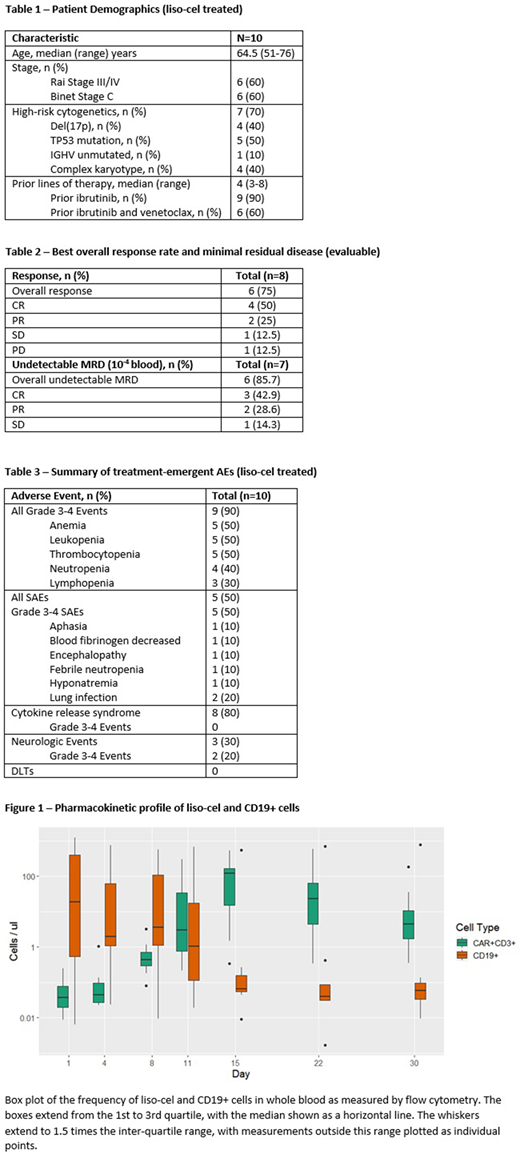
Median Cmax was 219 CAR T cells/µl (range 0.35-583.46). Median time to peak expansion was 15.5 days (range 13-19) and median AUC was 1528 cells*day/μL (range 590-2847). In the one pt with a best response of progressive disease, minimal CAR T cell expansion was observed. CAR T cells persisted in pts maintaining their response at 3 months post-dose.
Serum analysis showed elevated levels of multiple biomarkers, including CRP, IL6, PLGF, IL16, and IL15, in conjunction with CRS and NE.
Conclusion
Liso-cel toxicities were manageable, including events of CRS and NE, in these heavily pretreated pts with CLL. CRs and undetectable MRD were rapidly achieved in pts with both high-risk and standard-risk CLL who previously received ibrutinib, with the majority also having had received venetoclax. These preliminary data support continued development of single-dose liso-cel treatment in CLL.
Siddiqi:Juno Therapeutics: Other: Steering committee. Wierda:Genentech: Research Funding; AbbVie, Inc: Research Funding. Dubovsky:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Gillenwater:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Gong:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Mitchell:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Thorpe:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership. Yang:Juno Therapeutics: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal